The image quality can vary significantly between two 4K cameras, as pictured above, but why? Part of the answer is the camera sensor, which we looked at in detail in the last episode of our How To Video: Camera series.
However, a lot of the difference also comes down to what happens to the image data after it hits the sensor. There are three main factors: bit rate, bit depth, and chroma subsampling.
If you’re already lost, don’t worry. We’ll break down what each of those terms means, and how they impact footage quality. Watch the video below and keep reading to gain an in-depth understanding of what really makes a difference for pixel perfection.
Three Factors For Fantastic Footage
A lot goes into making a great-looking video. You need the right set, talent, lighting, hair and make-up, and more.
However, none of that matters if your video camera isn’t capturing all the details you so meticulously arranged. Watch as Nick LaClair, head of video production for SproutVideo, explains why bit rate, bit depth, and chroma subsampling are key to understanding the differences between footage quality from different cameras.
Better Bit Rate
In this context, bit rate refers to the amount of data the camera records per second. Cameras process tons of data about every single second of a video. After all, each second contains multiple frames composed of millions of bits of information.
Unsurprisingly, a higher bit rate equates to higher quality footage. It allows the camera to record more details about each frame.
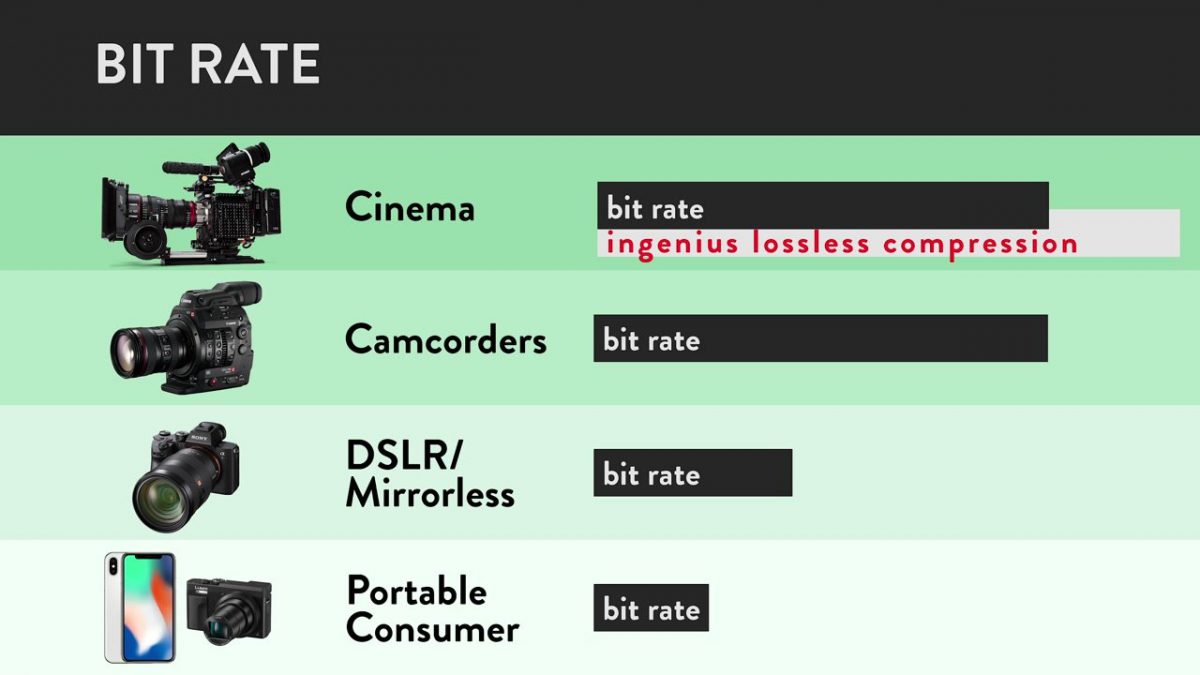
Still, bit rate only matters to a certain extent. The media the camera records to (e.g. a memory card or external drive) can only support up to a given bit rate. Once you hit that point, you no longer gain any benefits from higher bit rates. Here’s how that shakes down across different tiers of cameras:
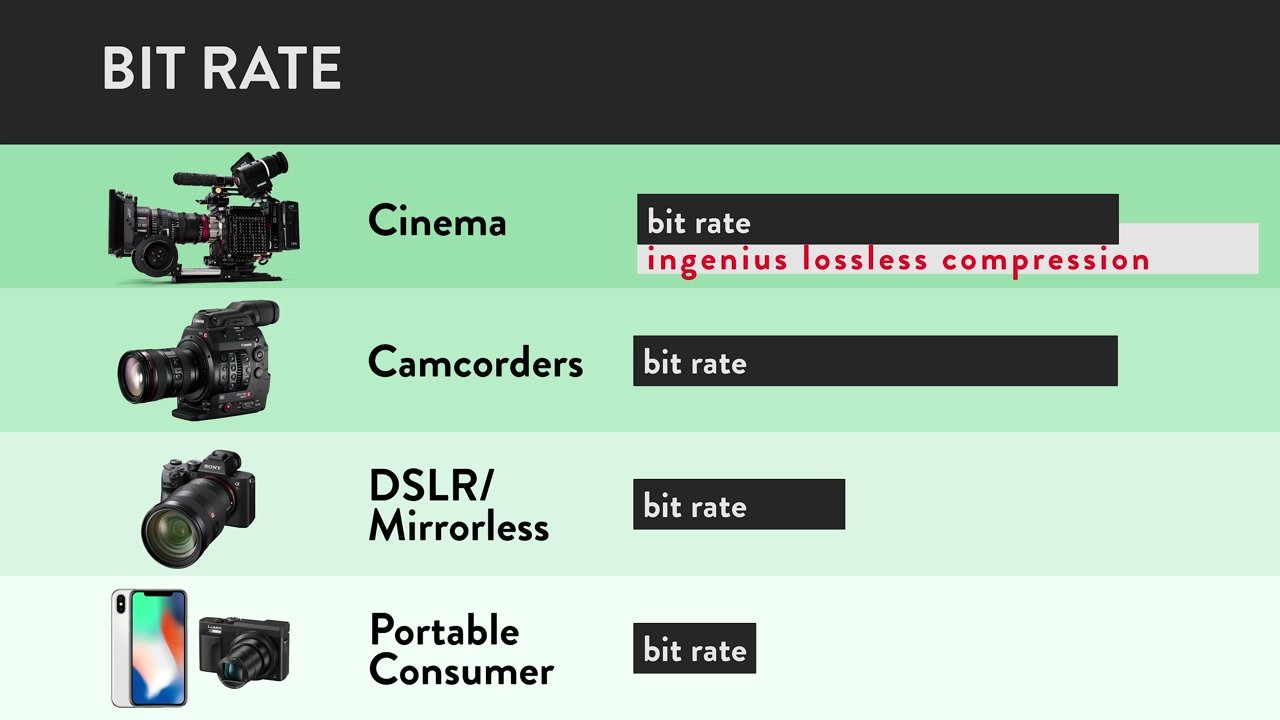
Once you hit the maximum bit rate the recording media can handle, bit rate levels off as a factor in image quality. When that happens, image compression becomes more important than bit rate for image quality.
Colorful Bit Depth
Bit depth is less well-known than bit rate, but every bit as important (see what we did there?). Bit depth refers to the number of colors your camera can read per pixel.
Common bit depths are 8-bit and 10-bit, which enable a camera to read 256 million or 1.07 billion colors respectively. That’s per pixel!
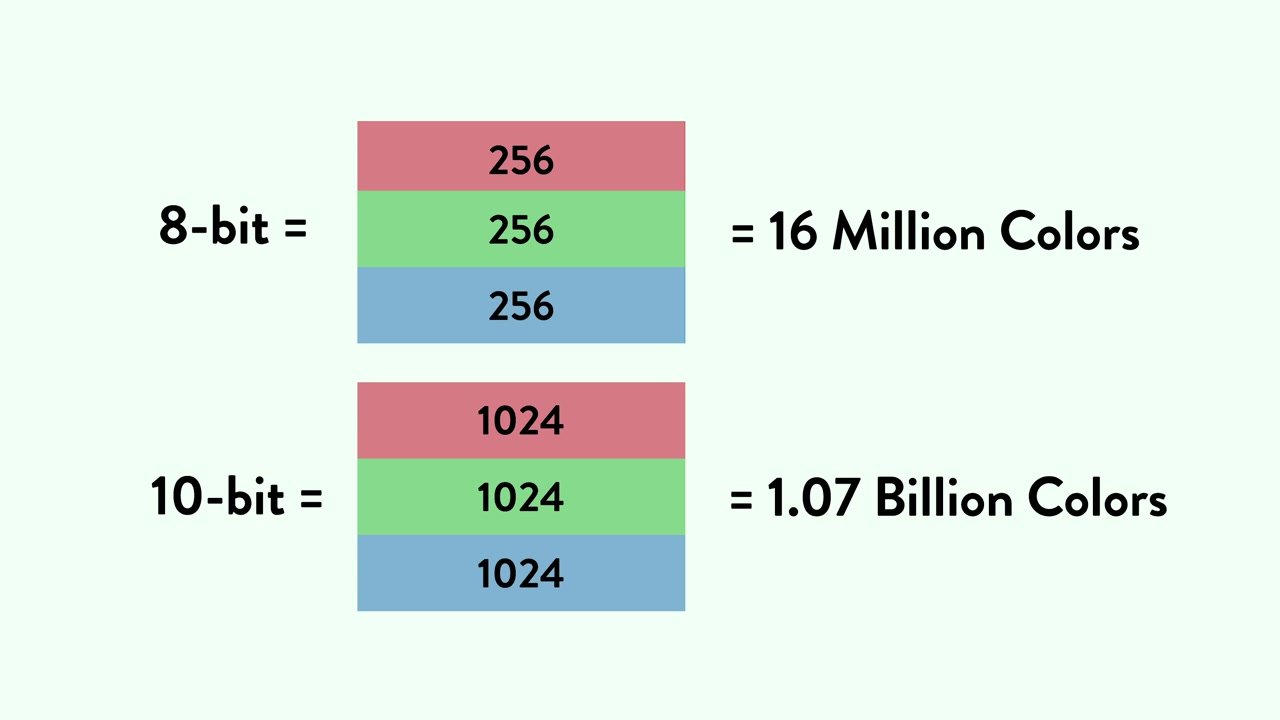
The more colors your camera can read, the more life-like the resulting image will appear. Higher end cameras typically offer greater bit depth than consumer options:
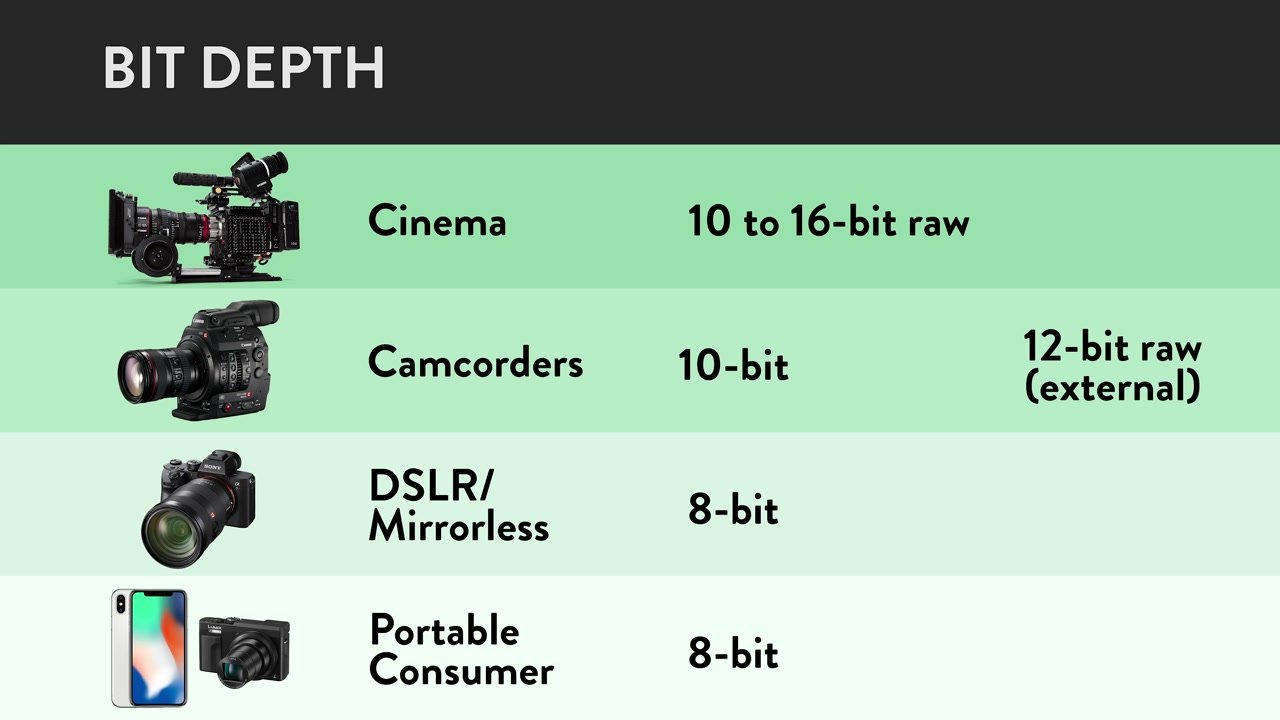
On some professional camcorders and cinema cameras, you can even bump up the bit depth when recording to external media. This enables you to capture even more colors per pixel than the camera supports otherwise.
Still, that’s not the whole story, because capturing all those colors requires a lot of processing power. That’s where chroma subsampling comes in.
Chroma Subsampling
Chroma subsampling sounds much more complicated than it is. Essentially, to save processing power, many cameras don’t capture color information about every single pixel. Instead, they fill in the gaps by “guessing” what’s in between.
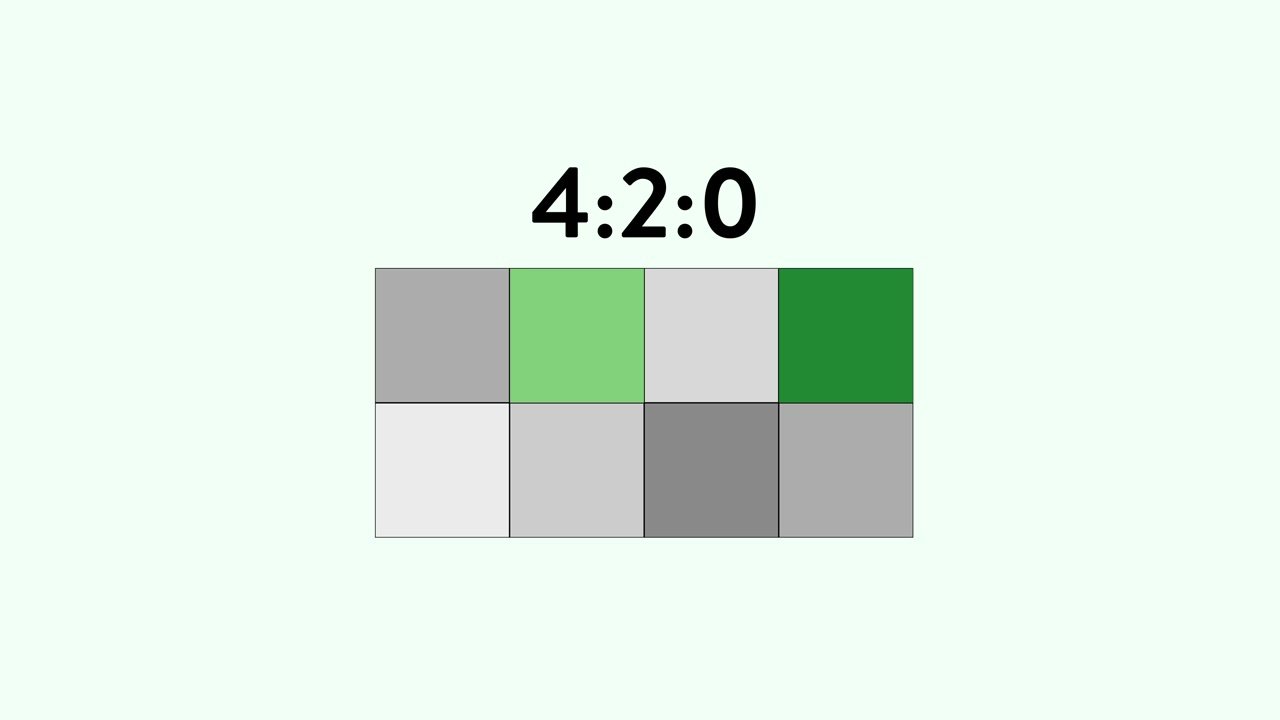
Most consumer cameras offer 4:2:0 chroma subsampling. It means that for the first row of four pixels, the camera will capture information from two of them. For the second row, it won’t capture any. Here’s what that looks like for each pixel:
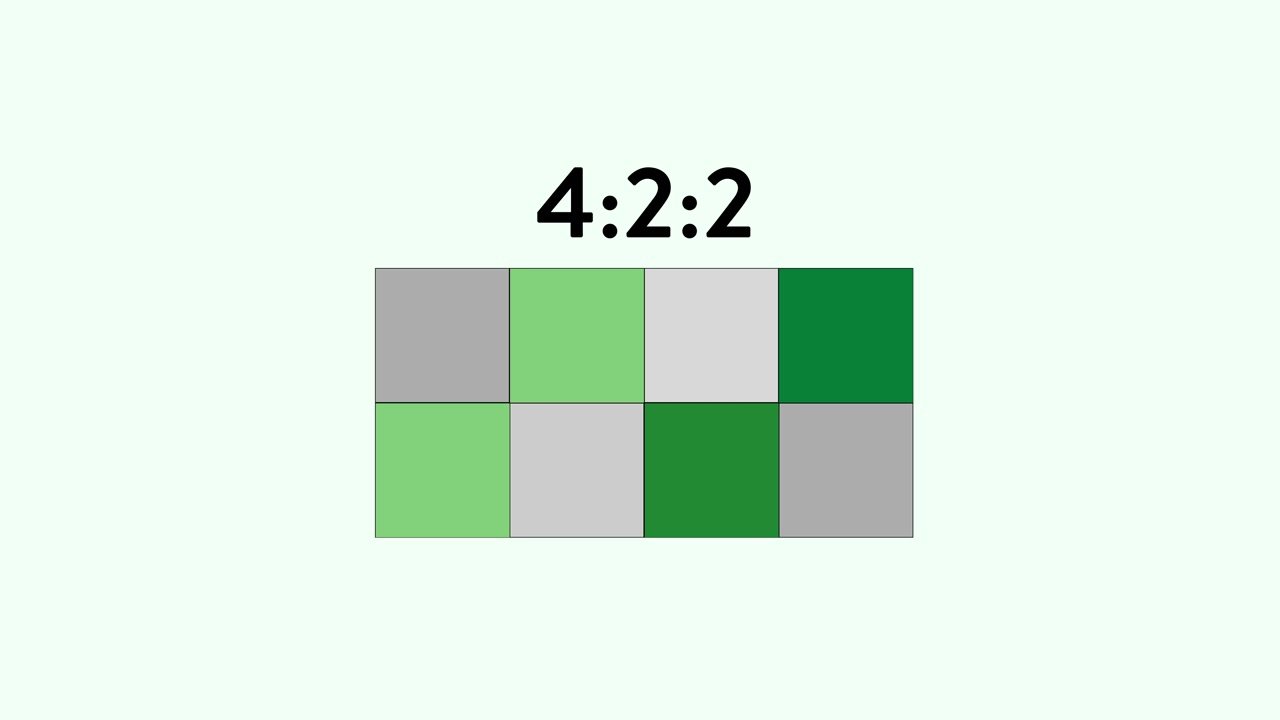
The next step up would be 4:2:2 chroma subsampling. In this case, the camera would capture color information from two pixels in each row of four.
And finally, in only the very top-of-the-line cinema cameras, you can find cameras that capture information from every single pixel. That’s referred to as 4:4:4 chroma subsampling, and it looks like this:

Adding to the complexity, and much like bit depth, you can often capture a higher quality of footage when recording to external media. Here’s how your chroma subsampling options break out across different tiers of cameras:
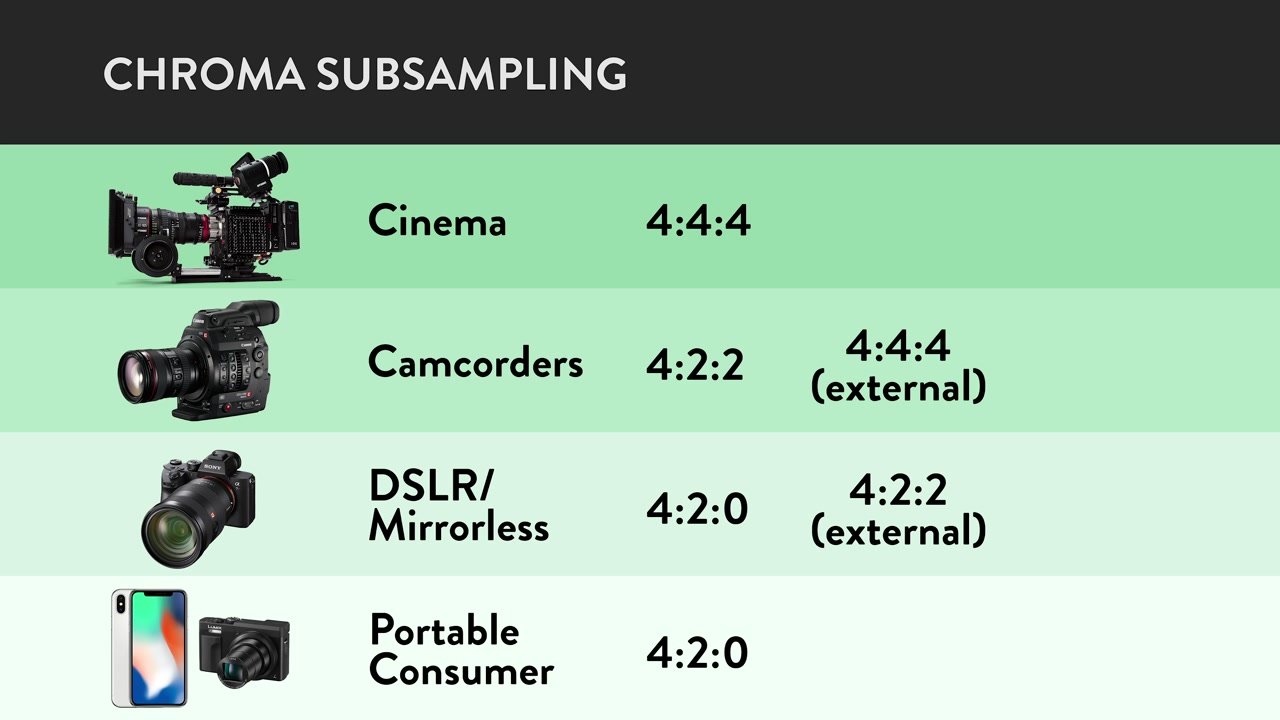
Bringing It All Together
A lot happens to the image the camera captures after it hits the sensor. The camera’s bit rate, bit depth, and chroma subsampling all impact the footage quality that results. By better understanding these factors for image quality, you can make a wiser choice when selecting your next camera for a video project.
Questions about image quality for video? Please share in the comments below!